Red Blood Cells (RBCs)
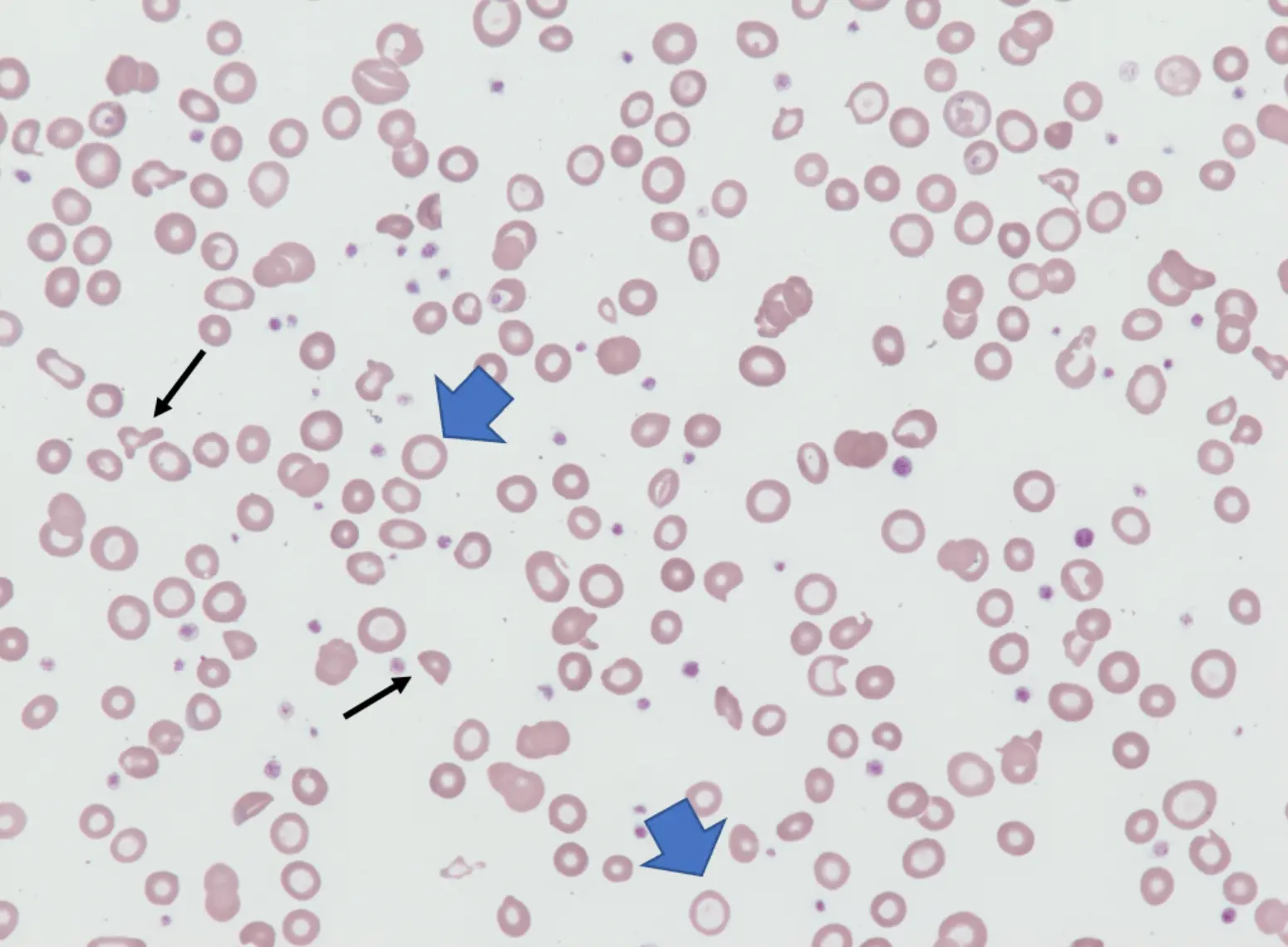
Red blood cells (RBCs), also known as erythrocytes, play a vital role in transporting oxygen from the lungs to the body’s tissues and removing carbon dioxide. Various disorders can affect RBCs, leading to different types of anemia and related symptoms.
Types of Red Blood Cells Disorders :
Iron-Deficiency Anemia:
Iron-deficiency anemia occurs when the body lacks sufficient iron to produce an adequate number of healthy red blood cells, leading to fatigue, weakness, and pale skin.
Vitamin B12 Deficiency Anemia:
Vitamin B12 deficiency anemia results from a lack of vitamin B12, crucial for red blood cell production, causing symptoms like fatigue, shortness of breath, and neurological issues.
Folate Deficiency Anemia:
Folate deficiency anemia arises due to insufficient folate intake, impairing red blood cell synthesis and causing symptoms such as fatigue, weakness, and difficulty concentrating.
Hemolytic Anemia:
Hemolytic anemia occurs when red blood cells are prematurely destroyed, either due to intrinsic defects or external factors, resulting in symptoms like jaundice, fatigue, and dark urine.
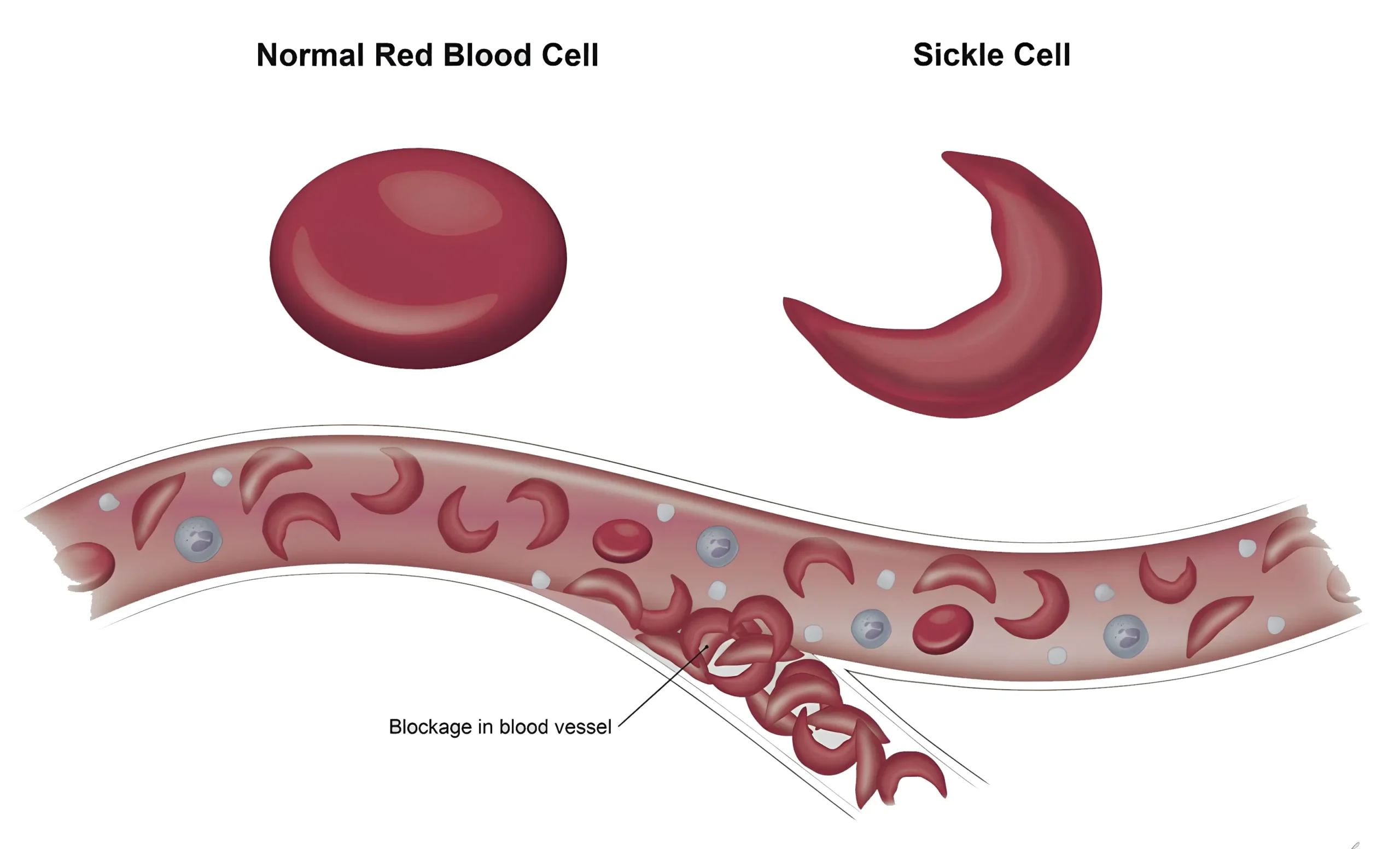
Sickle Cell Anemia:
Sickle cell anemia is a genetic disorder characterized by abnormal, sickle-shaped red blood cells that can obstruct blood vessels, leading to pain, anemia, and organ damage.
Common Symptoms:

Fatigue

Weakness

Shortness of breath

Pale skin

Dizziness

Rapid heartbeat
Treatments:
- Iron or vitamin supplements
- Dietary changes
- Blood transfusions
- Medications to stimulate RBC production or bone marrow transplantation
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the main symptoms of RBC disorders?
Symptoms vary depending on the specific disorder but commonly include fatigue, weakness, shortness of breath, pale skin, dizziness, and rapid heartbeat.
How are RBC disorders diagnosed?
Physical examination
Complete blood cell count
Special tests like hemoglobin electrophoresis, enzyme studies, membrane studies, bone marrow studies.
However all these special tests are individualised and done when indicated
Can RBC disorders be prevented?
Yes – Not only Nutritional Anemias can be prevented by dietary and lifestyle modifications like consuming iron-rich food, green vegetables, etc but also a Few conditions like Thalassemia can also be prevented by antenatal diagnosis.
Is sickle cell anemia treatable?
While there is no cure for sickle cell anemia, treatment options are available to manage symptoms, prevent complications, and improve quality of life. These may include medications, blood transfusions, and therapies to alleviate pain and reduce the risk of complications.
Are there any dietary changes that can help manage RBC disorders?
Yes, dietary changes can play a role in managing certain RBC disorders. For example, individuals with iron-deficiency anemia may benefit from increasing their intake of iron-rich foods such as red meat, poultry, fish, leafy greens, and fortified cereals. Similarly, those with vitamin B12 or folate deficiency anemia may require supplementation or dietary changes to address nutrient deficiencies.
Book an Appointment
Important Links
Contacting
Treatments
About Dr. Shraddha
Charity & Welfare
Happy Kids Foundation is a leading Non-Profit Organisation dedicated to help children for weaker socio-econimic backgrounds get the right treatments for Blood-related disorders. To get Involved / Volunteer / Donate, click the button below: