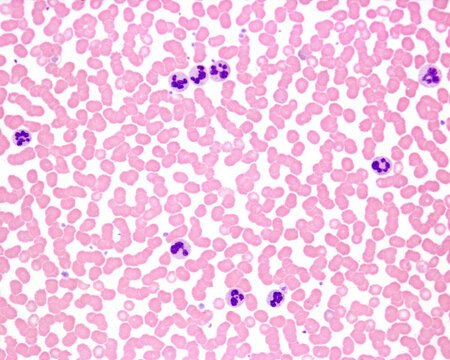
White Blood Cells (WBCs)
White blood cells, or leukocytes, play a crucial role in the body’s immune system, defending against infections and foreign invaders. Here’s a brief overview of WBC disorders
Types of White Blood Cells Disorders :
Leukocytosis :
This condition is characterized by an elevated level of white blood cells in the bloodstream. It often indicates an underlying infection, inflammatory response, or bone marrow disorder.
Leukopenia :
In contrast, leukopenia refers to a decrease in the number of white blood cells. This reduction weakens the body’s immune response, leaving individuals more vulnerable to infections.
Common Symptoms:
Symptoms of WBC disorders can vary depending on the specific condition but may include :

Fever

Fatigue

Weakness
Frequent Infections
Easy bruising or Bleeding
Swollen Lymph Nodes
Treatments:
- Antibiotics or antiviral medications to combat infections
- Corticosteroids to suppress inflammation
- Medications to stimulate white blood cell production
Frequently Asked Questions
What causes leukocytosis?
Leukocytosis is often caused by infections, such as bacterial or viral infections, inflammatory conditions like rheumatoid arthritis, allergies, leukemia, or as a response to certain medications.
What conditions can lead to leukopenia?
Leukopenia can result from viral infections (e.g., HIV), autoimmune disorders, bone marrow disorders, certain medications (e.g., chemotherapy), radiation therapy, or deficiencies in certain nutrients like vitamin B12 or folate.
How are WBC disorders diagnosed?
Diagnosis typically involves a physical examination, blood tests to measure white blood cell counts and differentials, and may require additional tests such as bone marrow biopsy or genetic testing for specific conditions.
Can WBC disorders be prevented?
While some WBC disorders may not be preventable, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, practicing good hygiene, avoiding exposure to infections, and seeking prompt medical attention for any concerning symptoms can help reduce the risk of developing certain conditions.
Is leukocytosis always a sign of infection?
While leukocytosis often indicates an infection, it can also be caused by other factors such as inflammation, stress, smoking, certain medications, or underlying medical conditions like leukemia. Evaluation by a healthcare professional is necessary to determine the underlying cause.
Book an Appointment
Important Links
Contacting
Treatments
About Dr. Shraddha
Charity & Welfare
Happy Kids Foundation is a leading Non-Profit Organisation dedicated to help children for weaker socio-econimic backgrounds get the right treatments for Blood-related disorders. To get Involved / Volunteer / Donate, click the button below: