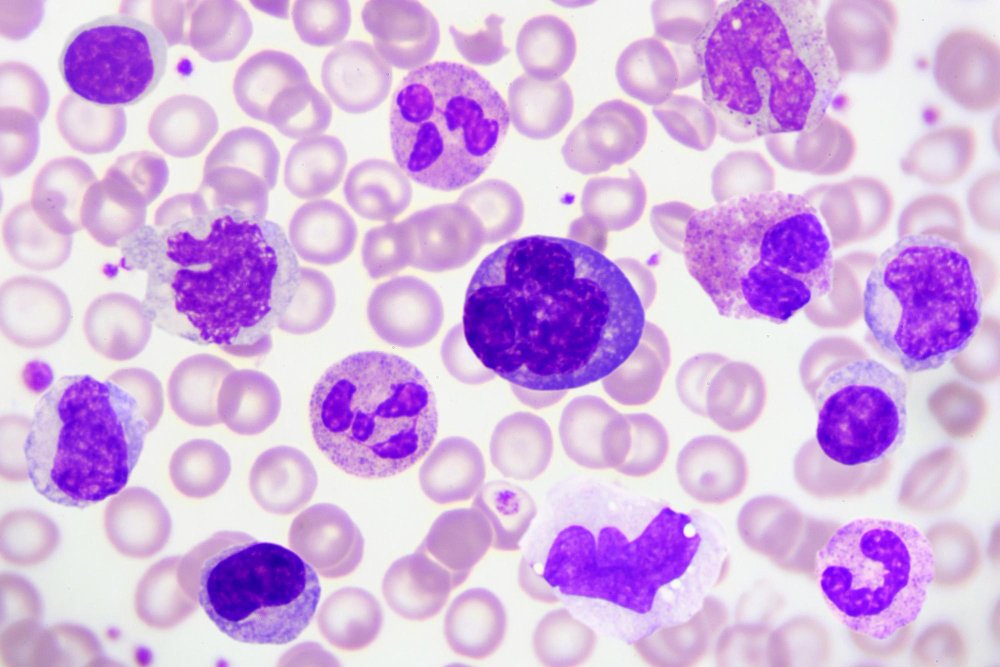
Benign Hematology
Benign hematology deals with non-cancerous blood disorders, unlike malignant conditions. It encompasses various conditions affecting blood components such as RBCs, WBCs, and platelets. These disorders, like anemia or thrombocytopenia, may arise from genetic or environmental factors. Treatment focuses on symptom management and preventing complications, often through medication or lifestyle changes. Regular monitoring is crucial for optimal management.
Types of Benign Hematology :
Red Blood Cells (RBCs):
Red blood cells (RBCs), also known as erythrocytes, play a vital role in transporting oxygen from the lungs to the body’s tissues and removing carbon dioxide. Various disorders can affect RBCs, leading to different types of anemia and related symptoms.
White Blood Cells (WBCs):
White blood cells, or leukocytes, play a crucial role in the body’s immune system, defending against infections and foreign invaders. Here’s a brief overview of WBC disorders
Platelets (Thrombocytes):
Platelets, also known as thrombocytes, are tiny blood cells that play a crucial role in blood clotting and wound healing.
Types of Benign Hematology :
Red Blood Cells (RBCs):
Red blood cells (RBCs), also known as erythrocytes, play a vital role in transporting oxygen from the lungs to the body’s tissues and removing carbon dioxide. Various disorders can affect RBCs, leading to different types of anemia and related symptoms.
White Blood Cells (WBCs):
White blood cells, or leukocytes, play a crucial role in the body’s immune system, defending against infections and foreign invaders. Here’s a brief overview of WBC disorders.
Platelets (Thrombocytes):
Platelets, also known as thrombocytes, are tiny blood cells that play a crucial role in blood clotting and wound healing.
Common Symptoms:

Fatigue and weakness

Shortness of breath

Paleness
Easy bruising and bleeding

Frequent infections
Enlarged spleen or liver
Bone pain

Jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes)
Treatments:
- Blood transfusions to replenish deficient blood components.
- Medications to stimulate red blood cell production or prevent blood clotting.
- Corticosteroids or immunosuppressive drugs to suppress the immune response in certain conditions.
- Splenectomy (surgical removal of the spleen) in cases of enlarged spleen or certain blood disorders.
- Lifestyle modifications and supportive care to manage symptoms and improve quality of life.
Frequently Asked Questions
What causes benign hematological disorders?
Benign hematological disorders can have various causes, including genetic factors, autoimmune conditions, infections, nutritional deficiencies, and certain medications.
Is treatment for benign hematological disorders lifelong?
The duration of treatment depends on the specific condition and its response to therapy. Some conditions may require ongoing treatment to manage symptoms and prevent complications, while others may resolve spontaneously or with short-term interventions.
Can benign hematological disorders be prevented?
While it may not be possible to prevent all benign hematological disorders, certain measures such as maintaining a healthy lifestyle, avoiding exposure to toxins or infections, and following recommended screening guidelines can help reduce the risk of developing certain conditions.
Are benign hematological disorders hereditary?
Some benign hematological disorders have a genetic component and may run in families. Genetic counseling and testing may be recommended for individuals with a family history of these conditions to assess their risk and explore preventive measures.
How can I manage symptoms of benign hematological disorders?
Managing symptoms often involves a combination of medical treatment, lifestyle modifications, and supportive care. It’s essential to work closely with your healthcare team to develop a personalized management plan tailored to your specific needs and goals.
Book an Appointment
Important Links
Contacting
Treatments
About Dr. Shraddha
Charity & Welfare
Happy Kids Foundation is a leading Non-Profit Organisation dedicated to help children for weaker socio-econimic backgrounds get the right treatments for Blood-related disorders. To get Involved / Volunteer / Donate, click the button below: